Systems Practice
Omidyar Systems Thinking
“Systems Practice Workbook.” Observatory of Public Sector Innovation, 20 Feb. 2019, oecd-opsi.org/toolkits/systems-practice-workbook/.
Through a process of set phases, a direct approach is set to map a complex problem and gain clarity. Specific points in the system are identified and analyzed to determine where the largest impacts can be made to make a systematic change.
Launch
Development of a guiding star and near star define the area of focus.
The framing question serves as understanding of the system that will be analyzed and affected throughout the systems practice journey.
Explore Forces
The core forces of the system are identified and categorized as an inhibitor of the system or enabler. These forces are then divided into major themes to be further analyze in the next step.
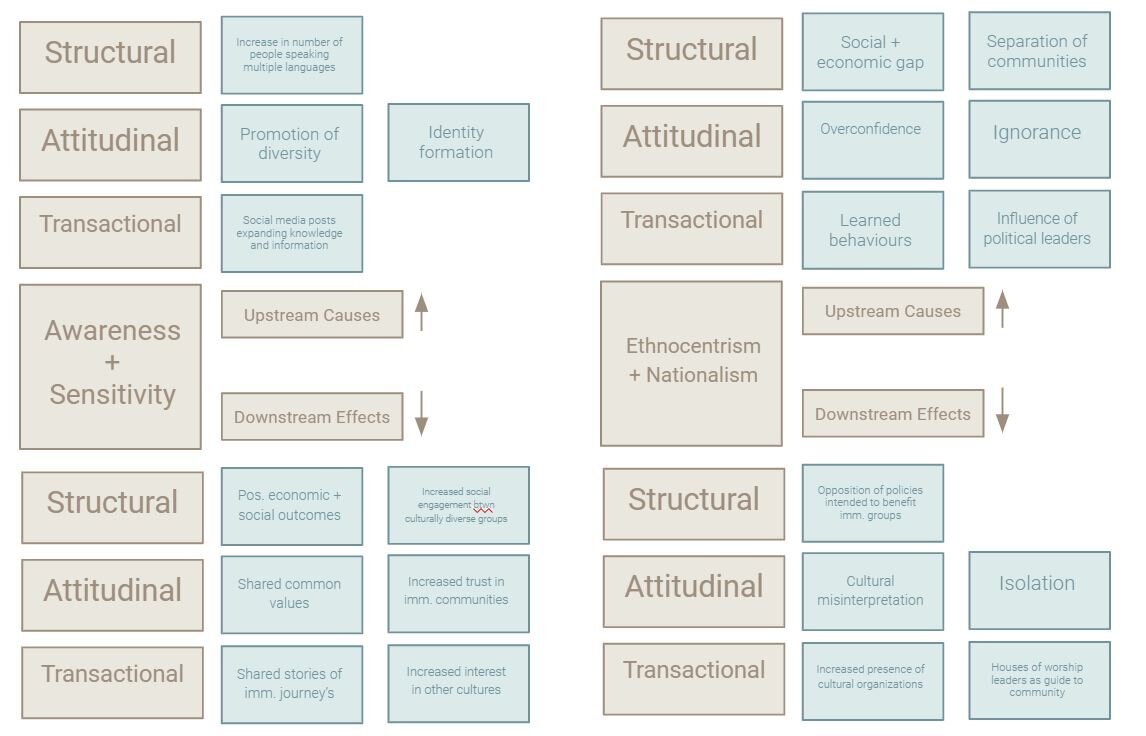
Causes and Effects
The themes that define the forces are analyzed. The upstream causes and downstream effects are identified. The causes and effects are divided into a category: structural, attitudinal, or transactional.
Create Loops
Patterns in the forces, causes and effects are analyzed. Forces that drive the system are interrelated and can be tied together in feedback loops.
Discover the Deep Structure
The deep structure serves as a connecting point for all other loops. The most important and repeating elements in the individual loops are further analyzed and synthesized into the deep structure.
Immigrants are essential to the evolution of western culture, however, there is a conflict between US economic prosperity and maintenance of cultural identity.
Systems Map
Individual loops are brought together and combined to create a systems map that outlines the major drivers of the overall system. The systems map provides a template to holistically look at and impact the system.
The deep structure is supported through political, material, religious and cultural responses. Immigration supports US prosperity through strengthening the job and housing markets. Accessibility of resources promotes social engagement. Resource allocation is crucial, competition for resources is at the root of hostility towards immigrant groups. Religious centers are necessary in supporting immigrant groups and providing a source of comfort and stability. Maintenance of cultural identity supports mental health and well-being, often times, pressures of assimilation can cause mental distress. Every immigrant group influences and forms western culture and identity, often spread through popular culture. Addressing and sharing the realities of immigration will create understanding of diverse cultural groups and how they have formed western culture.